SD WAN
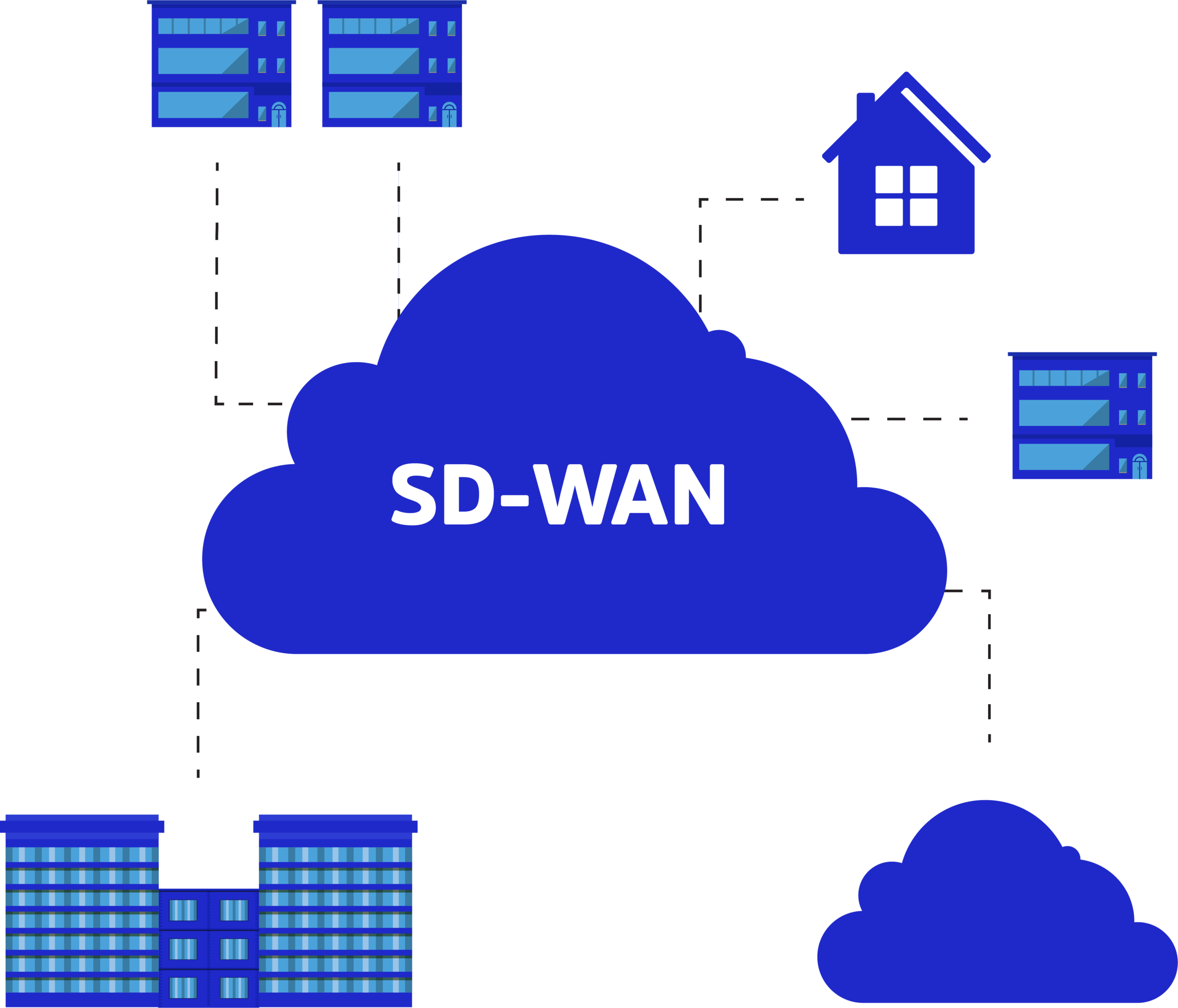
SD-WAN (software-defined wide area network) is a type of networking technology that uses software-defined networking (SDN) principles to manage and optimize the performance of wide area networks (WANs). It enables organizations to securely connect users, applications and data across multiple locations while providing improved performance, reliability and scalability. SD-WAN also simplifies the management of WANs by providing centralized control and visibility over the entire network.
How Does SD-WAN Work?
SD-WAN is a virtualized service that connects and extends enterprise networks over large geographical distances. WANs use links such as multiprotocol label switching (MPLS), wireless, broadband, virtual private networks (VPNs) and the internet to give users in branch and remote offices access to corporate applications, services and resources, allowing them to work regardless of location. SD-WAN also monitors the performance of WAN connections and manages traffic in an effort to maintain high speeds and optimize connectivity.
Traditional WANs use legacy routers to connect remote users to applications hosted in data centers. A router is mostly command line interface (CLI) driven. To define where and how the data egresses a branch network utilizing traditional WAN, network engineers and administrators must manually write rules and policies. Such procedures are frequently time-consuming and error-prone.
SD-WAN is designed to solve the multiple challenges associated with traditional WAN, allowing networking professionals a simpler way to optimize and secure WAN connectivity. SD-WAN is based on software rather than hardware and is configured to handle different kinds of traffic and conditions in real-time. It can adapt quickly to changing situations and offer better security and reliability than traditional WANs.